Oncology
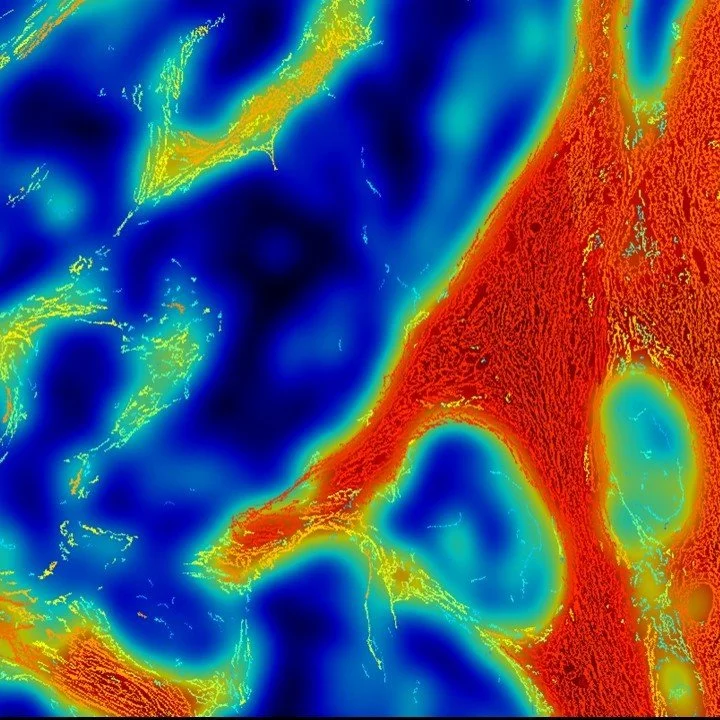
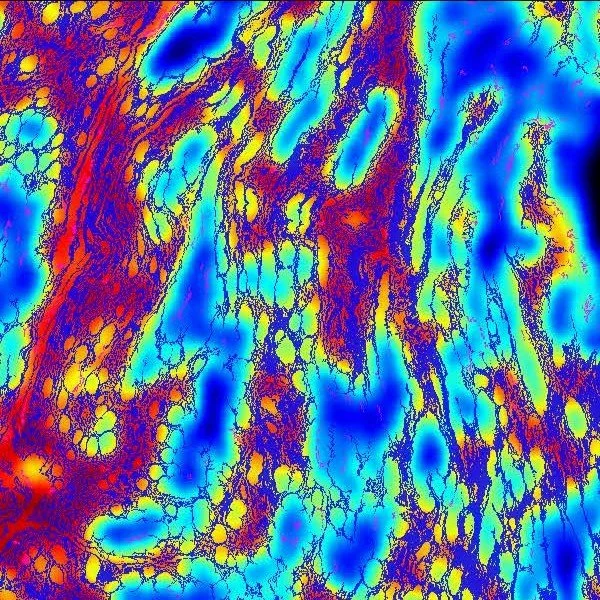
Quantifying fibrosis in the extracellular matrix (ECM) reveals how stromal remodeling drives tumor progression, immune exclusion, and therapy resistance. Objective ECM metrics stratify disease stage and prognosis by capturing collagen density, alignment, and stiffness. Measuring fibrosis guides antifibrotic and immuno-oncology strategies, helping overcome the tumoral fibrotic barrier to immune infiltration and drug delivery.
fibrotypes predict LYMPH NODE METASTASIS and colon cancer outcomes
Quantitative fibrosis phenotyping in advanced colon cancer revealed that digital assessment of collagen structure and organization can accurately predict lymph-node metastasis and recurrence. Using FibroNest™, phenotypic fibrosis composite scores distinguished metastatic and recurrent cases with high sensitivity and specificity, demonstrating fibrosis quantification and fibrotypes as a powerful biomarkers for prognosis and therapeutic stratification.
Intratumoral Fibrotic Features are Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Recurrence in Patients with Advanced Colon Cancer. Mine et Al. Modern Pathology - (38),11, November 2025, 100828
FIBROTYPES Distinguish HCC RIKS in PATIENTS WITH NAFLD
Quantitative fibrosis analysis using FibroNest™ identified distinct fibrotypes in cirrhotic NAFLD livers with and without HCC. Automated Ph-FCS scoring differentiated HCC with high accuracy by integrating collagen structure, morphometry, and architecture. This FibroNest approach i poised to enhances early detection, risk stratification, and precision assessment of hepatocarcinogenesis in fibrotic livers.
Automated fibrosis phenotyping of liver tissue from non-tumor lesions of patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nakamura et Al. Hepatol Int. 2022;16(3):555-561.
CCN1-Driven Fibrosis Fuels Melanoma Progression
Cancer-associated fibroblast–specific CCN1 expression promotes melanoma progression by enhancing angiogenesis, collagen organization, and metastatic potential. Loss of CCN1 disrupted ECM structure and vascular formation, reducing metastasis. These findings highlight stromal CCN1 and high-resolution fibrotypes as valuable tools for identifying therapeutic targets and predicting resistance to immunotherapy.
Cancer-associated Fibroblast–specific Expression of the Matricellular Protein CCN1 Coordinates Neovascularization and Stroma Deposition in Melanoma Metastasis. Hutchenreuther et Al. Cancer Research Communications (2024) 4 (2): 556–570.